BFS | JavaScript
September 9, 2023
AlgorithmBFS
BFS
이전에 포스팅했던 DFS처럼 BFS 또한 완전탐색 알고리즘 중 하나입니다. Breadth(폭)라는 단어처럼 인접한 노드부터 방문합니다.
간선의 비용이 동일한 상황에서 최단거리 문제를 해결해야하는 경우(다익스트라 최단 경로 알고리즘과 유사한 경향이 있습니다.), 완전 탐색을 위해 DFS가 메모리/시간 초과를 받아 BFS로 재시도해야하는 경우 BFS를 사용합니다.
큐(Queue) 자료구조를 이용해서 BFS를 구현할 수 있습니다.
큐 (Queue)
큐 자료구조를 이용해서 BFS를 구현할 수 있기 때문에, BFS를 먼저 구현하기 전에 큐에 대해서 공부해보겠습니다.
큐는 "줄"이라는 뜻으로, 표를 구매하려고 온 사람이 줄 서있는 모습을 생각하면 간단합니다. 먼저 온 사람이 표를 먼저 구매할 수 있는 선입선출의 자료구조입니다.
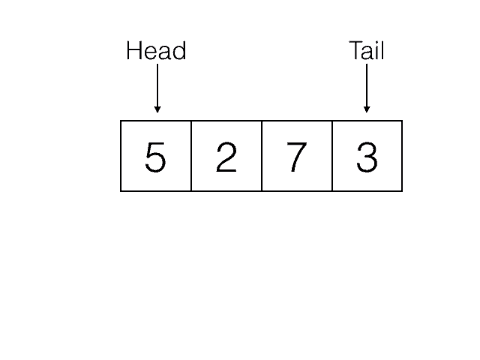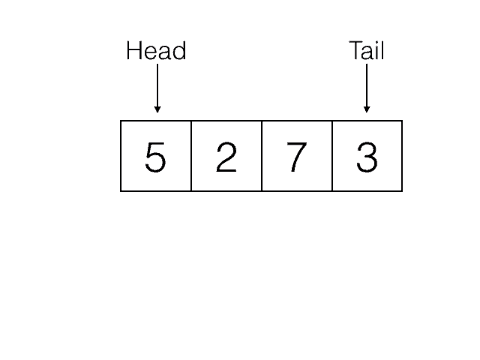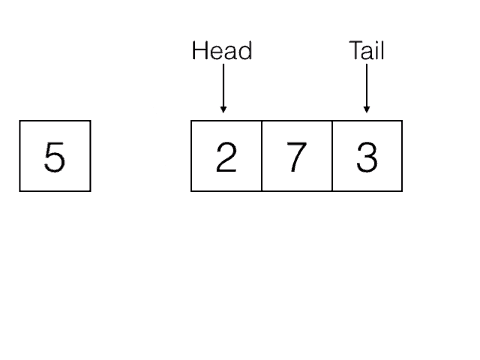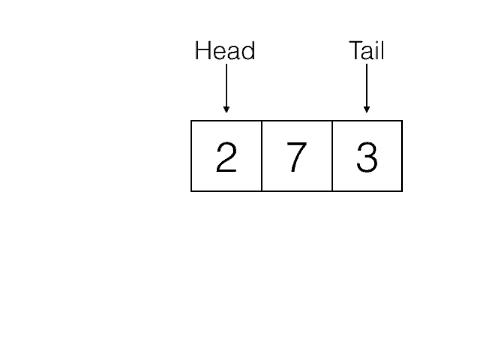
const queue = [];
queue.push("FIRST");
queue.push("SECOND");
queue.push("THIRD");
// queue = ["FIRST", "SECOND", "THIRD"]
queue.shift(); // FIRST
queue.shift(); // SECOND
queue.shift(); // THIRD위 코드처럼 배열을 이용해 간단히 큐를 구현할 수 있지만, 배열에 만 개의 요소가 있다면 인덱싱을 재조정해야 되기 때문에 성능상 좋지 않습니다. 성능을 신경써야하는 상황이라면, 직접 큐 클래스를 만드는게 좋습니다.
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.first = null;
this.last = null;
this.size = 0;
}
enqueue(val) {
var newNode = new Node(val);
if (!this.first) {
this.first = newNode;
this.last = newNode;
} else {
this.last.next = newNode;
this.last = newNode;
}
return ++this.size;
}
dequeue() {
if(!this.first) return null;
var temp = this.first;
if (this.first === this.last) {
this.last = null;
}
this.first = this.first.next;
this.size--;
return temp.value;
}
}BFS 구현
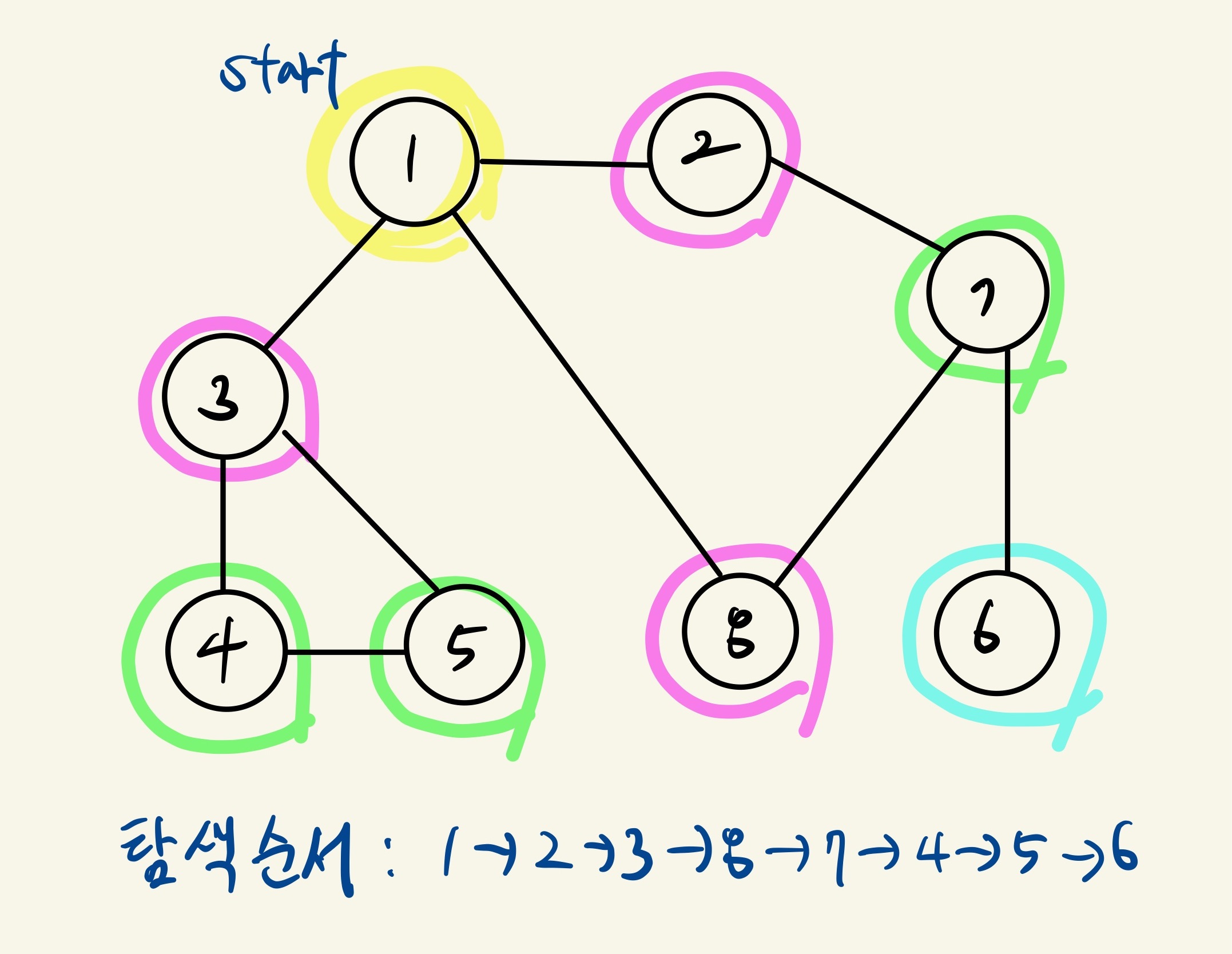
// 그래프 구현
const graph = [
[],
[2, 3, 8],
[1, 7],
[1, 4, 5],
[3, 5],
[3, 4],
[7],
[2, 6, 8],
[1, 7],
];
// 각 노드 방문 여부
const visited = new Array(9).fill(false);
function bfs(start) {
// 큐 생성
const queue = [];
queue.push(start);
// 현재 노드 방문처리
visited[start] = true;
// 큐가 빌때까지 반복
while (queue.length !== 0) {
const v = queue.shift();
console.log(v);
for (i of graph[v]) {
if (!visited[i]) {
queue.push(i);
visited[i] = true;
}
}
}
}
bfs(1);
// 출력순서 : 1 2 3 8 7 4 5 6